Fortran Allocate Array In Subroutine

Stack Overflow In Fortran 90 Stack Overflow

Automatic Fortran To C Conversion With Fable Source Code For Biology And Medicine Full Text
Faculty Washington Edu Rjl Classes Am5s13 Slides Am5lecture8nup3 Pdf

Fortran An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Basics Of Fortran Course Notes

The Fortran 90 Programming Language Book Chapter Iopscience
Interfaces to Fortran 77 style routines must only use Fortran 77 style constructs.

Fortran allocate array in subroutine. Note, the scalar. Maybe you want to call a library routine that expects to get a vector, but you have the data to be passed stored in a matrix. (A) ALL(MASK) is true if all elements of MASK are true.
It depends how you declare the subroutines variables, if they are deferred shape and you have explicit interfaces (e.g. I am new to fortran. You can determine how much space to allocate to your merge array by using the SIZE intrinsic function to get the size of each of the two arrays that will be merged.
Copy the data from the temporary to the newly allocated array 4. KEY => PARA (K :. There are instances where one wishes to change the rank (the number of dimensions) of an array as it is passed to a subroutine.
If one wants an efficient list in Fortran 95 (including TR's), with the ability to append elements, I think one needs to define a derived. In the old days, the maximum size arrays had to be declared when the code was written. I try to write a small program to allocate a variable in small subroutine and i've passed it, now i allocate array in a loop or many loops but i don't have any ideas about it.
Also apparent is. This modified text is an extract of the original Stack Overflow Documentation created by following contributors and released under CC BY-SA 3.0. Arrays One-dimensional Arrays.
Fortran 90 and later. I'd like to say that C doesn't really support arrays, but let's not put it that way. Since I am not knowledgeable about the mechanics of passing allocatable arrays to a subroutine, if I were doing this program, I would do all of the work in the main program, at.
Make a simple complete code that shows the 'error' and post it and you will get some specific advice. Deallocation is as follows:. RESULT = SIZE(ARRAY, DIM , KIND) Arguments:.
ALLOCATABLE Attribute and Statement Dynamic Objects NULLIFY Statement POINTER Attribute and Statement Pointers Related Intrinsics:. Subroutine set (m, u, v, w) Class (Multia), Intent (InOut) ::. The dyn array END FUNCTION How to use a function that returns a pointer:.
A (:,:) ALLOCATE (A (-1:. Because y, i, and j were declared after x and hence happen to occupy memory after x, these values are corrupted by the subroutine. K + LGTH) Related Topics:.
Creation of the descriptor. Note, the SCALAR= keyword and allocatable scalar entities are available in Fortran 03 and later. Main Question or Discussion Point.
However, in Fortran, a pointer is a data object that has more function. Defining functions that return an array Functions in Fortran 90 can return an array !. This descriptor is used both for assumed-shape and deferred-shape arrays.
Start date May 6, 12;. Allocate array R = A( location(1), :. The subroutines are in modules) then the compiler will know the array bounds by default and would throw an error.
It was a common extension to Fortran77 to allow declarations of the form LOGICAL*1, INTEGER*2, or REAL*8. 9.15 ALLOCATED — Status of an allocatable entity Description:. Thus, a question arises as to what happens.
The rank of the array, i.e., the dimensions has to be mentioned however, to allocate memory to such an array, you use the allocate function. If REALLOCATE is defined in Fortran, it will certainly need to apply to multidimensional arrays. Hi Guys, I'm a beginner in fortran programming and don't speak english so well, but i hope you will undersand my question ;) In the program there is an allocatable array, which shall be allocated in the subroutine, and then given back to the main program (beacause in the subroutine i read in the data and get to know how big the array must become).
I'll say instead that arrays are much more fundamental to Fortran than to C (and even more so to f90 than they were to f77). Allocate ( darray(s1,s2) ) After the array is used, in the program, the memory created should be freed using the deallocate function. Developer Guide and Reference.
Fortran codes that solve real engineering problems often have tens of thousands of lines. Humongous array then Fortran 03 offers the move_alloc intrinsic which moves the allocation (including the values) from one variable to another. Or to arrays allocated to a pointer.
Syntax ALLOCATE (allocation-list , STAT=stat-variable) Where:. Furthermore, the shape and size of the result array returned by the function is determined at run time. For the array matrix, it is 9, and for the array numbers, it is 5.
A pointer is associated with a target by allocation or pointer assignment. 9)) END SUBROUTINE SUB. In this example, it is permitted to leave out the interface altogether since routines without interfaces are treated as Fortran77 style routines by default.
The only way to handle such big codes is to use a modular approach and split the program into many separate smaller units called subprograms. It is the number of elements an array contains. Thread-local and global arrays are supported.
Program exp_realloc implicit none integer,allocatable,dimension(:,:)::. Declaring a Pointer Variable. The following program illustrates dynamic memory allocation and array-based operations, two features introduced with Fortran 90.
Fortran - Pointers - In most programming languages, a pointer variable stores the memory address of an object. Deallocate the temporary." I would like to see how the subroutine to append elements to a 1-D array would be written with MOVE_ALLOC. For instance, if you allow up to 300 variables, matrices of up to 0 x 0 elements, you want to truncate it down to.
Fortran 95 and later. He probably does not want to bother the caller to figure out how much storage to allocate and do the allocation. And then allocate the array inside the subroutine once the appropriate header records that inform me how much data there are have been read.
Dynamic memory allocation and arrays. The shape of an array is a one-dimensional integer array, containing the number of elements (the extent) in each dimension. Return the C_LOC of the allocated array (1).
9.253 SIZE — Determine the size of an array Description:. It is a simple code to pass an array to a subroutine and print it, but doesnt behave that way:. Allocate(x(npts)) Call Sub1(x) End Program Main.
07/15/ Public Content Download as PDF. Each allocatable or pointer array in the allocation-list will have a list of dimension bounds, ( lower-bound : upper-bound , ) upper bound and lower-bound are scalar INTEGER expressions. This was a great disadvantage, as it resulted in wasted RAM (arrays size had to be the maximum possible) or in frequent recompilations.
Allocate ( darray(s1,s2) ) After the array is used, in the program, the memory created should be freed using the deallocate function deallocate (darray) Example. Allocation of the Fortran side would search the array of arrays/pointers (link to next node if/when necessary) and when unallocated array is found (or pointer not associated), then use that entry for the allocation. Return pointer to !!.
It would look like this:. The address of x is passed to the subroutine, which interprets it as the address of the starting point of an array of length 3. ALLOCATED ASSOCIATED To Read More About It:.
Consider the following Fortran code SUBROUTINE SUB INTEGER, ALLOCATABLE::. This assigns the values of the A array in column order similar to the rules of Fortran 77. The rank of the array, i.e., the dimensions has to be mentioned however, to allocate memory to such an array, you use the allocate function.
ALL(MASK) returns a scalar value of type LOGICAL where the kind type parameter is the same as the kind type parameter of MASK.If DIM is present, then ALL(MASK, DIM) returns an array with the rank of MASK minus 1. For large scale general purpose programs, like a statistical analysis package, we have to allocate large arrays to handle the design capacity for numbers of variables, size of analysis, etc. For example, for the array matrix, shape is (3, 3) and the array numbers it is (5).
ALLOCATED(ARRAY) and ALLOCATED(SCALAR) check the allocation status of ARRAY and SCALAR, respectively. Functions that return arrays Functions in Fortran 90 can even return arrays (or matrices) !. If an argument to the subroutine is an array, it must also be declared as an array in the subroutine.
Allocated(array) and allocated(scalar) check the allocation status of array and scalar, respectively. Fortran 90 and later, with KIND argument Fortran 03 and later. A vector is an (n 1) or (1 n)matrix,ascalarisa(11) matrix, a string is a vector of double precisionnumbers which happen to be ASCII codes.
Is it allowable to have a module with declared allocatable arrays used by the main program where they are allocated and then pass them to a subroutine where they have an assumed size?. Mathematical operations are applied to the array as a whole. Calling Fortran From Matlab 4 In Matlab 4, that is actually all there is (except for symbolic arrays, about which I don’t know anything).
To ensure that enough memory is available to allocate space for your array, make use of the STAT option of the ALLOCATE command:. 1991, Fortran Standard, 6.3.1, 6.3.3. Advanced Array-Passing in Fortran.
In the subroutine, he wishes to allocate the array, set values into the array and return it to the caller. Long before ALLOCATE/DEALLOCATE, we had to do memory allocation in assembly language. So, if an argument to the subroutine is real in the main program, it must also be real in the subroutine.
From the point of view of a source code reader all aspects of the array can now be presented in quite a compact manner. Subroutines and Functions When a program is more than a few hundred lines long, it gets hard to follow. Where the Allocs module would be:.
The subroutine sets the value of x to 5 and also sets the values of the next 2 memory locations (based on 8-byte real numbers) to 5. Intel® Fortran Compiler 19.1 Developer Guide and Reference. May 6, 12 #1 luonganh.
Determine the extent of ARRAY along a specified dimension DIM, or the total number of elements in ARRAY if DIM is absent. The shape is determined from the shape of MASK where the DIM dimension is elided. The actual subroutine refers to a Fortran 77 explicit shape array.
In addition to basic types, you can also vary the precision of real arrays according to the precision of Abaqus/Explicit and define arrays of user-defined data types. Find row + column !!. Here gfortran will allocate in the stack a local variable A for a descriptor of rank 2 and then it initializes it with the proper values.
Function name clashes - Fortran has no reserved words, but problems may arise one of your external function names matches that of an intrinsic function. Allocation-list is a comma-separated list of pointer or allocatable variables. Please see the following code.
Copy pivot row pivot_row => R !!. Fortran90 allows for "allocatable" arrays. The lesson here is:.
R = ALLOCATE( SIZE(A(1, :) ) !!. E.g., shape and size of the array can be derived using values from the input parameters. Fortran - Allocate array in subroutine Fortran;.
Furthermore, the size of the array (or matrix) returned by the function can be defined using values that are derived from the input parameters This feature is extremely useful when you write functions that return matrices or vectors, whose size depends on the size of input. Pointers to char arrays ALLOCATE (PARA (1000) ). Fortran 90 addressed this further with the use of assumed shape arrays - the array shape is also automatically "passed" across with the array data.
If the object of an ALLOCATE statement is an array, the ALLOCATE statement defines the shape of the array. Particularly noteworthy is the absence of DO loops and IF/THEN statements in manipulating the array;. Arrays and Parallel programming in Fortran 90/95 Allocatable Arrays.
I want to create a Fortran 90 subroutine that reads data from a file, and returns it in an array, which is one of the arguments to the subroutine. To facilitate data accumulation and transfer between user subroutines, you can use utility functions to create your own dynamic storage in the form of allocatable arrays. Syntax to define a function that returns an array:.
Write a program that calculates the difference in area between two triangles.

Subroutines An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 024 Formats Arrays Allocate Limits Of Int Youtube

4 Infrastructure Fields And Grids

1 5 Dynamic Arrays

Solved Scc374c 394c Parallel Computing For Science And E Chegg Com

Fortran 90 Tutorial Tutorial Simples Em Fortran Docsity

Non Allocated Array For Optional Argument With Cheks Turned On

Let Us Use A Subroutine Instead Of A Function U Chegg Com

Data Structuring In Fortran Springerlink

Displaying Fortran Module Data Totalview User Guide V6 3

Blog Posts

Dynamically Sizing Arrays Degenerate Conic

Intel Fortran Libraries Reference Maxloc Array Mask Manualzz
2
Faculty Washington Edu Rjl Classes Am5s13 Slides Am5lecture8nup3 Pdf

Fortran Gdb Debugging Wrong Array Values Vscode
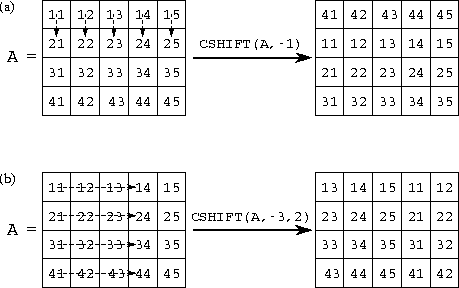
7 2 Fortran 90

Introduction Modern Fortran Short
Faculty Washington Edu Rjl Classes Am5s13 Slides Am5lecture8nup3 Pdf

Ppt Fortran 90 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Passing Pointer To Subroutine Intel Community

Example Of Fortran Code And Device Variable Point Wise Expression Download Scientific Diagram
Http Www Star St And Ac Uk Pw31 Compastro Lecture 5 Pdf
Http Homepages Ulb Ac Be Gmelard Si Cs09ch1 Pdf
2

Up To Date Admin Magazine 39 17

A Basic Introduction To Programming In Fortran

Fortran Quick Guide Tutorialspoint

7 2 Fortran 90
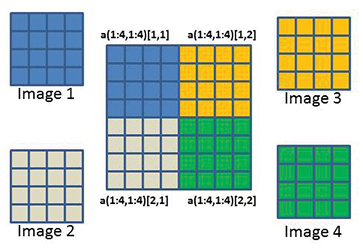
Up To Date Admin Magazine 39 17
Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 038 Determinant Using Subroutines And Functions Youtube

Let Us Use A Subroutine Instead Of A Function U Chegg Com

Subroutine Return An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
2
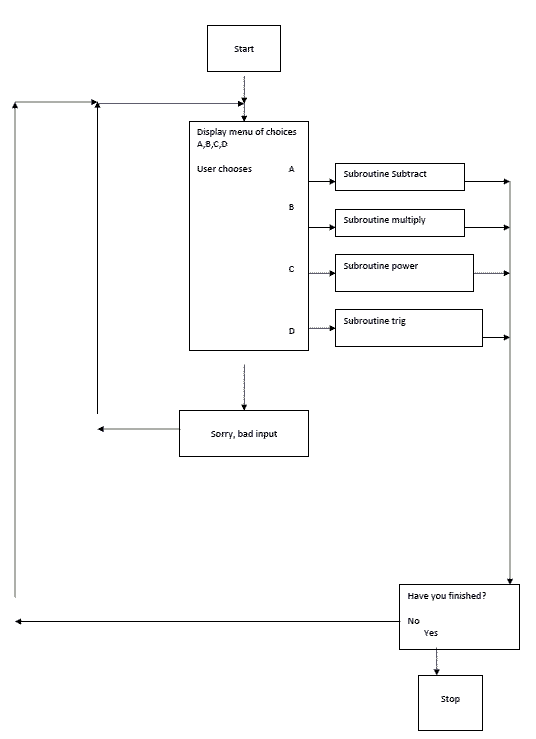
Fortran Tutorial Free Guide To Programming Fortran 90 95 Advanced Topics

Fortran 90 95 And Fortran 90 Generalities Format Changes Portable Numerics Arrays Syntax Classes Of Arrays Dynamic Storage Structures Ppt Download

Uni Texus Austin

Stack Overflow On Subroutine Call Only When Compiled With Intel Visual Fortran And Fine When Compiled By Compaq Visual Fortran Stack Overflow

The Fortran 90 Programming Language Book Chapter Iopscience

Pass A Fortran Derived Type Which Contains Allocatable Array Between Different Compilers Pgi And Intel Stack Overflow
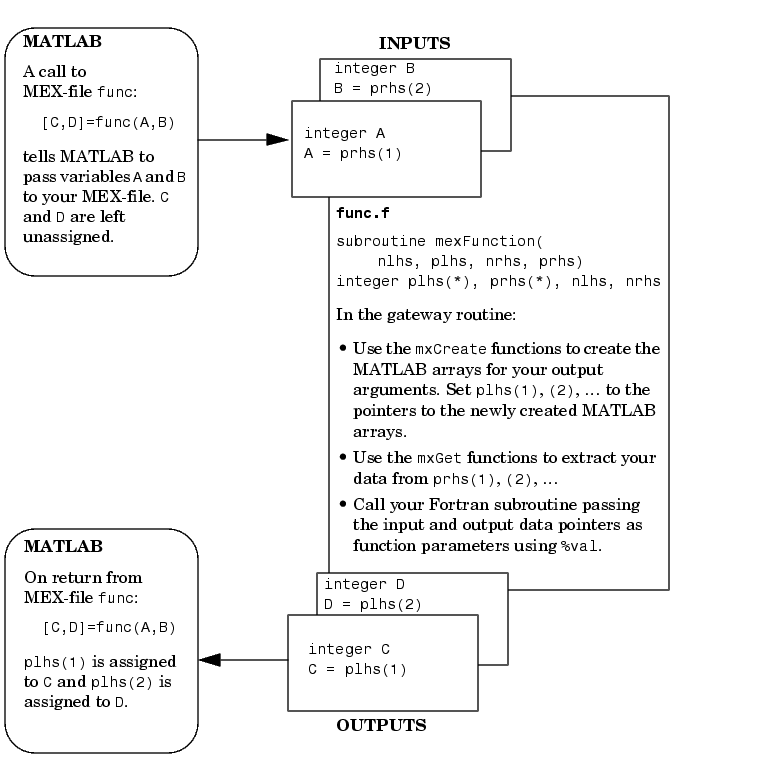
Creating Fortran Mex Files External Interfaces Api

Pdf Generic Programming In Fortran 90 Arjen Markus Academia Edu

Example Of Fortran Code And Device Variable Point Wise Expression Download Scientific Diagram

Fortran 90 Arrays

Example Illustrating The Handling Of Common Variants By Emulating The Download Scientific Diagram

Analyzing Stock Price Time Series With Fortran Arrays Part 2 Manning
Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 024 Formats Arrays Allocate Limits Of Int Youtube
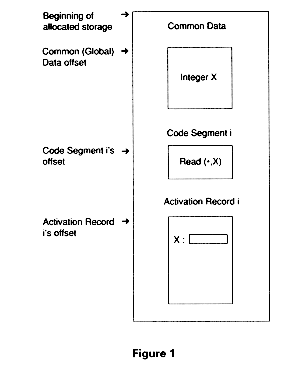
12 3 6 Static Storage Allocation
Http Homepages Ulb Ac Be Gmelard Si Cs09ch1 Pdf

Basics Of Fortran Course Notes

Computers In Engineering Comp 8 Subprograms Subroutines

Ch 13 Array Processing And Matrix Multiplication Ppt Download

Fortran Subroutine Parameter Computer Programming

Subroutines 2 Springerlink
Introduction To Fortran Ppt Download
Http Www Star St And Ac Uk Pw31 Compastro Lecture 5 Pdf

1 5 Dynamic Arrays

Fortran Array Allocation Overflow Stack Overflow
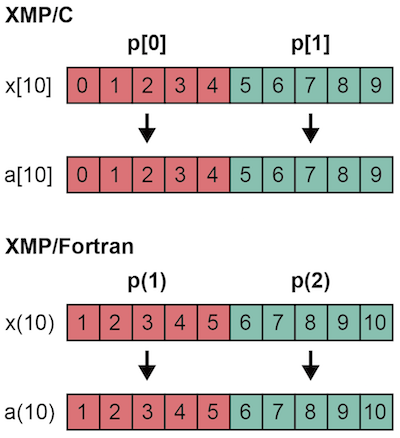
23 Procedure Interface Xcalablemp Handbook 1 0 Documentation

Blog Posts
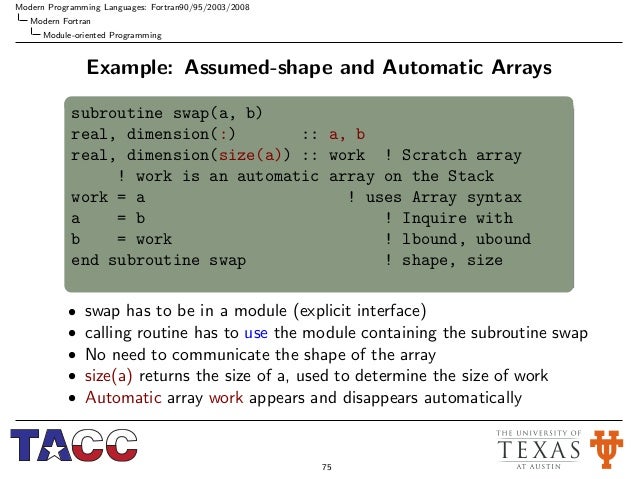
Uni Texus Austin

Data Structuring In Fortran Springerlink

Let Us Use A Subroutine Instead Of A Function U Chegg Com

Analyzing Stock Price Time Series With Modern Fortran Part 3 Milan Curcic

Fortran 90 Deferred Shape Array Types

Alps Algorithms And Libraries For Physics Simulations
Http Www Star St And Ac Uk Pw31 Compastro Lecture 5 Pdf
Returning Array From Function Issue 114 Fortran Lang Stdlib Github

Ppom A Nested Scalable Parallel And Fortran 90 Implementation Of The Princeton Ocean Model Sciencedirect

Problems With Allocatable Arrays Real8 Accessing Ranges Not Allocated In Arrays In Fortran Intel Community
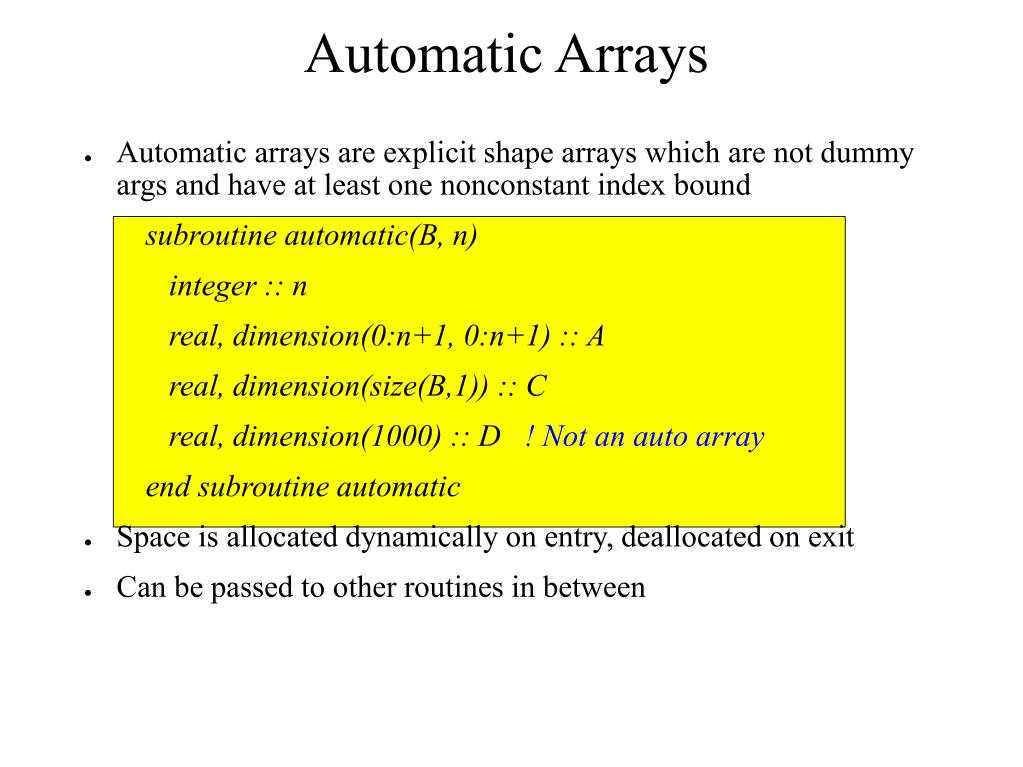
Ppt Fortran 90 95 And 00 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Fortran 90 Features Ohio State University Fortran 90 Features 4 Fortran 90 Objectives Language
Analyzing Stock Price Time Series With Modern Fortran Part 2 By Milan Curcic Modern Fortran Medium

Fortran 90 Features Ohio State University Fortran 90 Features 4 Fortran 90 Objectives Language Pdf Document
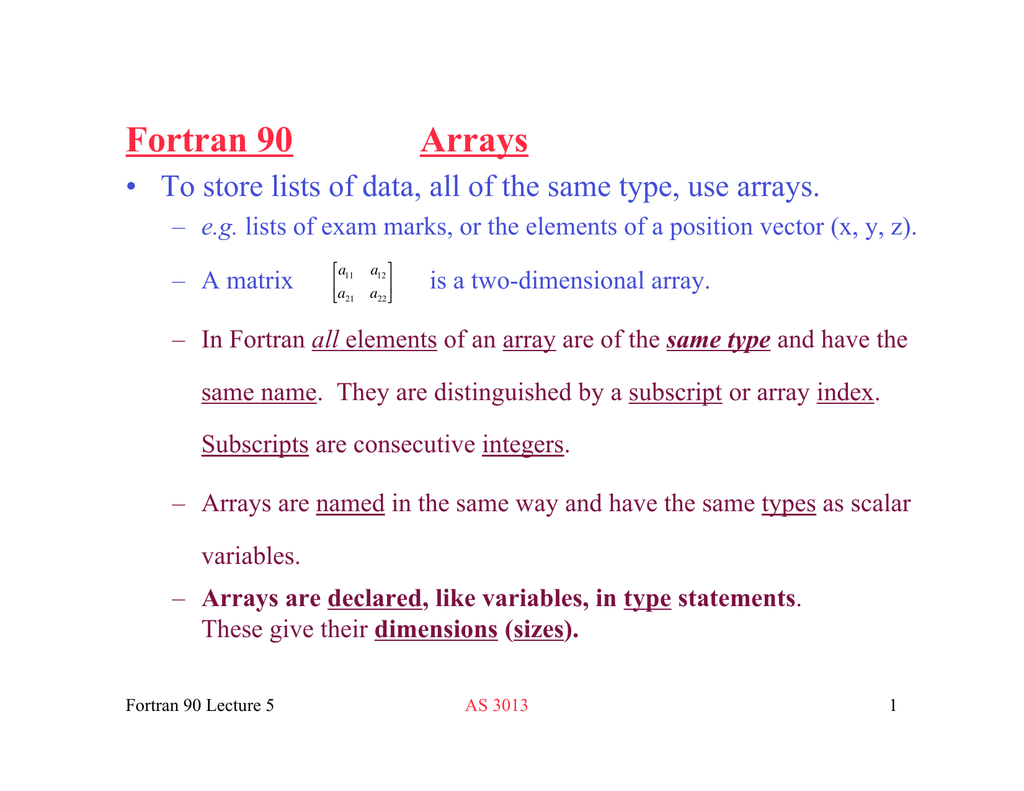
Fortran 90 Arrays

Fortran 90 Pointer Types Totalview User Guide V6 3

Fortran 90 Gotchas Part 3 Acm Sigplan Fortran Forum

Alps Algorithms And Libraries For Physics Simulations

Nd Serial Fortran Example

Lahey Lf Pro 7 8

Grib1
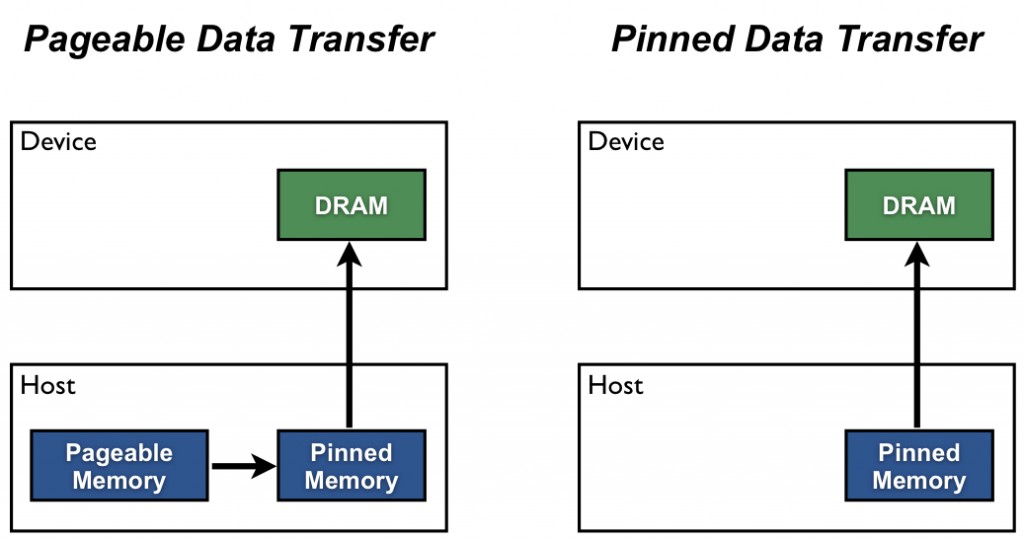
How To Optimize Data Transfers In Cuda Fortran Nvidia Developer Blog

Errores Fortran Subroutine Pointer Computer Programming

Introduction To Fortran
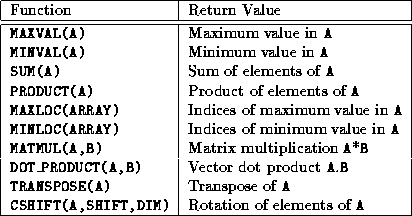
7 2 Fortran 90

Subroutines 2 Springerlink

Problems With Allocatable Arrays Real8 Accessing Ranges Not Allocated In Arrays In Fortran Intel Community

Cypress Programming Fortrancpp Hpc
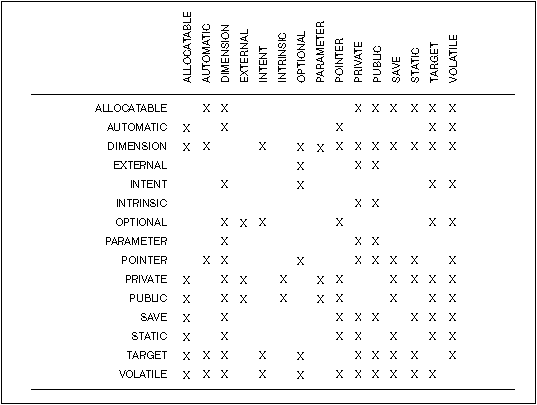
Language Reference

Rqhemoh8jlhenm
2
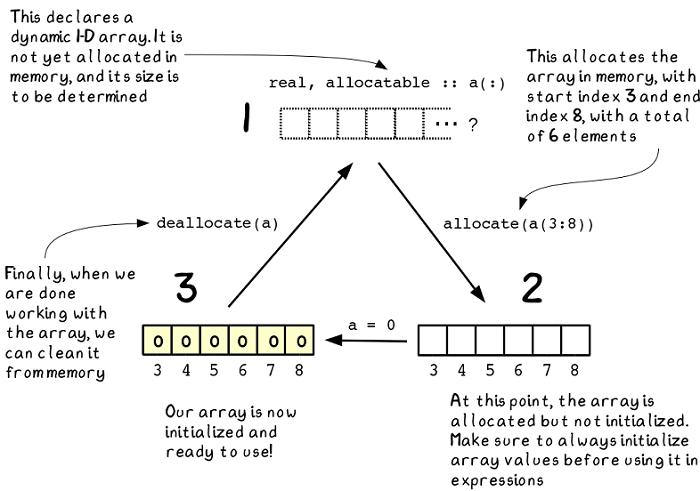
Analyzing Stock Price Time Series With Fortran Arrays Part 2 By Manning Publications Medium
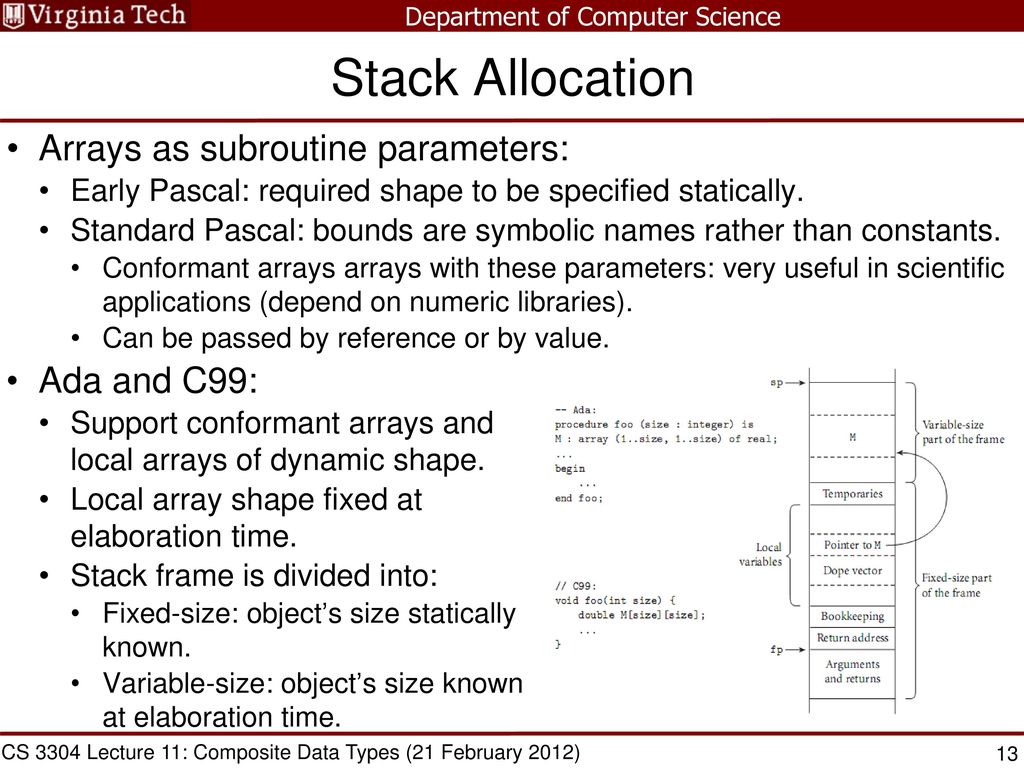
Cs 3304 Comparative Languages Ppt Download

Dynamic Array Gets Corrupted In Fortran Stack Overflow



