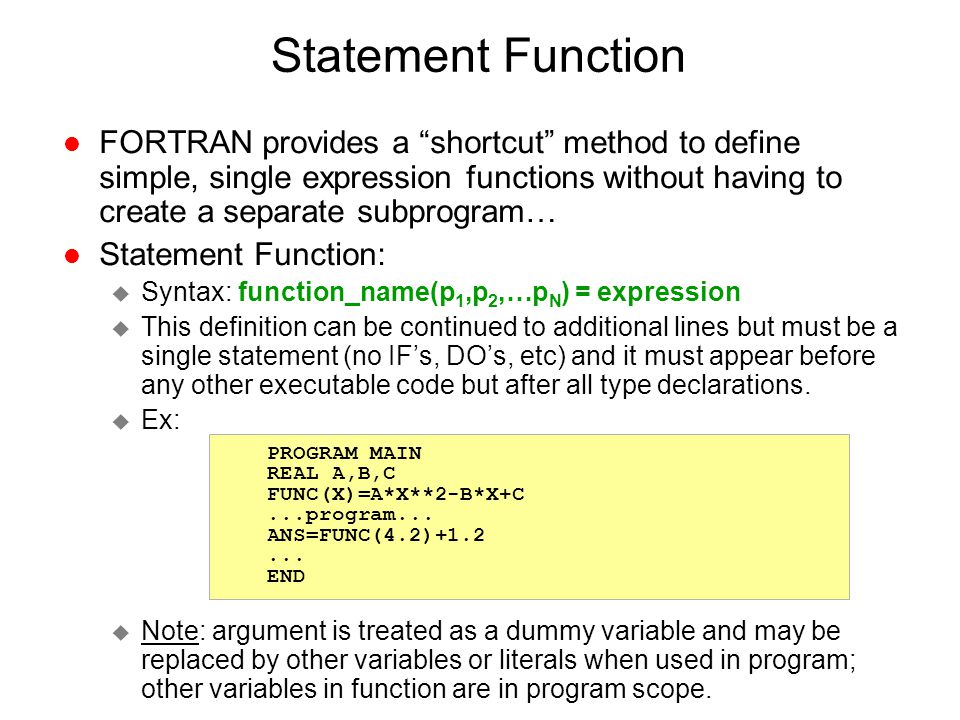
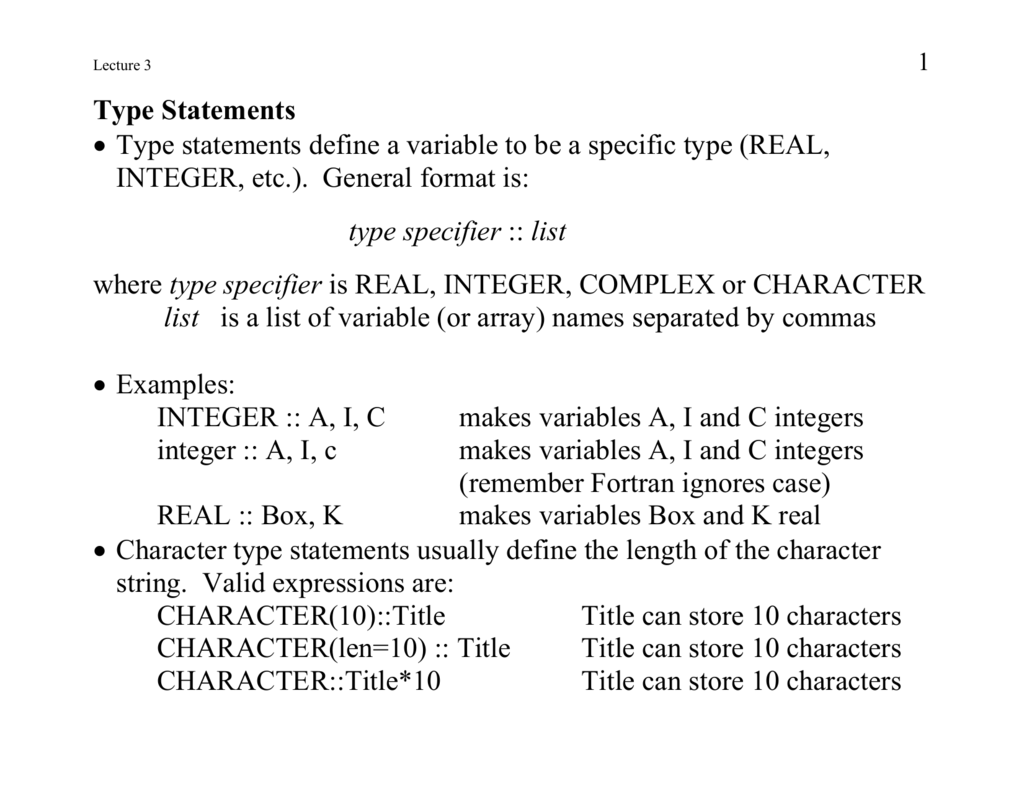
Fortran Type Statement
Q Tbn 3aand9gctnl9a42lrqi6aemsorvcf5hajnlyy1adluopx Rj2hjgpqq2ie Usqp Cau

Fortran Tutorial
2

Fortran 90 Reference Card Cheat Sheet

Fortran Quick Guide Tutorialspoint

Technical Report No 5 Brlesc S Ll Fortran Lloyd W Campbell Glenn A Beck March Pdf Free Download
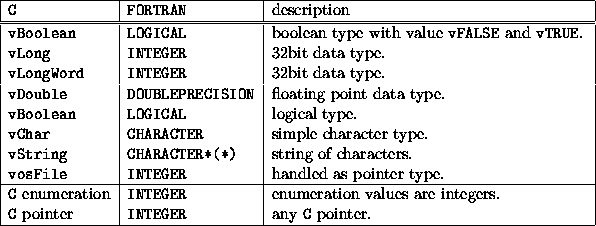
(Fortran 03 adds new types for C interoperability.) Arrays.

Fortran type statement. Kind, basically, defines internal representation of the type:. This creates an unnamed field. The number 7 in the WRITE statement refers to the statement number of the corresponding FORMAT statement.FORMAT statements may be placed anywhere in the same program or function/subroutine block as the WRITE.
Confirm or to override the type established by default or by the IMPLICIT statement. The form of an arithmetic IF statement is:. FORTRAN 66 Interpretation of the EXTERNAL Statement Alternative Syntax for the PARAMETER Statement Alternative Syntax for Binary, Octal, and Hexadecimal Constants.
After you have declared a user-defined type by using the Type statement, you can declare a variable of that type anywhere within the scope of the declaration. A TYPE IS type guard statement matches the selector if the dynamic type and kind type parameter values of the selector are the same as those specified by the statement.;. The USE statement makes a module of precompiled declarations available to a program unit.
FORTRAN IV removed the machine-dependent features of FORTRAN II (such as READ INPUT TAPE), while adding new features such as a LOGICAL data type, logical Boolean expressions and the logical IF statement as an alternative to the arithmetic IF statement. For the three numeric types, it defines the precision and range, and for the other two, the specifics of storage representation. Fortran 90/95 provides a versatile and safe mechanism for making global information available to program units through the MODULE.
In Intel Visual Fortran, we provide a number of modules that declare Windows API interfaces. An extending derived type inherits type bound procedures from the parent, but this can be overriden. UNIT = 5 for INPUT from the keyboard with the READ statement UNIT = 6 for OUTPUT to the screen with the WRITE statement Most versions of FORTRAN will also let you use the ASTERISK (*) for I/O to the TERMINAL.
It also provides a means of renaming or limiting the accessibility of entities in the namespace. Labels can range from 1 to. (The card reader or keyboard was usually connected as unit 5).
The following labels are valid:. The same statement label must not be given to more than. The FORTRAN IV compiler is itself a computer program that examines FORTRAN IV statements and tells the com.
Subsequent statement block is executed. Disclaimer and legal information information in this document is provided in connection with intel(r) products. StepValue is optional , the.
Use Dim, Private, Public, ReDim, or Static to declare a variable of a user-defined type. In this example each write statement used a different format statement. The following rules and behavior apply to type declarations in record structures:.
ZTherefore, PROGRAM, end, IF, then, DO, etc may be used as identifiers. Fortran 90 has no concept of unsigned integers, nor 1 byte or 2 byte integers. 5.2.5 TYPE Statement 5.2.6 WRITE Statement 5.2.7 READ Statement 5.2.8 REREAD Statement 5.2.9 ACCEPT Statement 5.3 Device Control Statements 5.4.
4-26 Chapter 5 Specification Statements. A type guard statement cannot be a branch target statement. However, type statements can be preceded by an IMPLICIT statement.
Override the length by one of the acceptable lengths for that data type. The default implicit typing rule is that if the first letter of the name is I, J, K, L, M, or N, then the data type is integer, otherwise it is real. All FORTRAN programs have the following format:.
It is permissible to branch to an end-select-type-stmtonly See Type Guard (Fortran 03)for syntax details. %FILL can be specified in place of a field name to leave space in a record for purposes such as alignment. If a FORTRAN statement (not a comment line) is too long it may be extended onto the next line if a character other than a 0, space, or !.
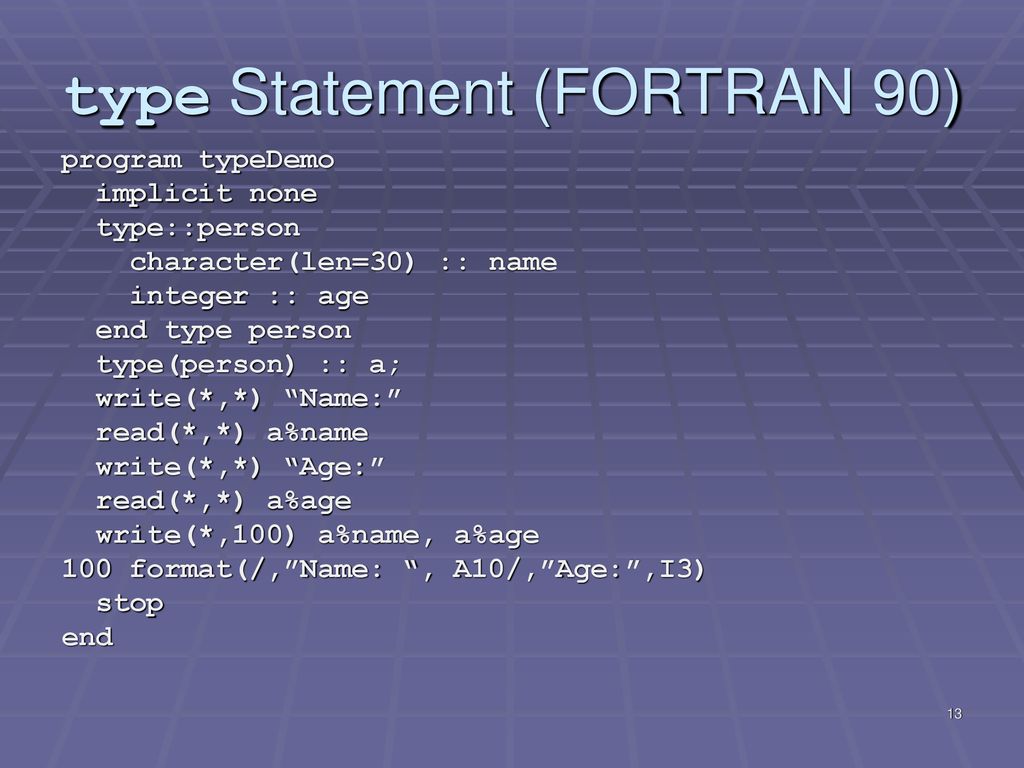
A derived data type is also called a structure, and it can consist of data objects of different types. The USE statement makes the specified namespace accessible to the current scoping unit. Fortran allows you to define derived data types.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to. Note that double precision constants using the “d” suffix are also obsolescent, as appending an underscore and the appropriate kind value is more portable. A variable in a module that is not saved becomes undefined when.
123 5000 1 0001 The last two labels are equivalent. Statement Purpose The INTERFACE statement is the first statement in an interface block. Type1 is the class prototype name contains.
Standard FORTRAN reserves two UNIT numbers for I/O to user. Statement Labels Fortran statements can have labels consisting of one to five digits, at least one of which is non-zero. Integer, real, complex, logical, and character.
ZYes, end = program + if/(goto – while)is legal!. It has a single, signed integer type, typically of 4 or 8 bytes. It immediately follows the SUBROUTINE, FUNCTION or PROGRAM statements.
Zfunction-name isaFortran90identifieris a Fortran 90 identifier. Derived Data Types The Fortran 90 derived data type is similar to C structures and also has some similarities with C++ classes. Other attributes of the associating entity are described in Associate names.
Initialization in a DATA statement or in a type declaration implies that a variable has the SAVE attribute, unless the variable is in a named common block in a block data subprogram. Fortran 77 has only one type for integer variables. The free format simple I/O has the form −.
In the early days of FORTRAN, when computer memory was measured in kilobytes, this was a valuable technique to make the most efficient use of very limited memory. Fortran keywords as identifiers. The construction of an equivalent MODULE block for a COMMON block is quite straightforward.
FORTRAN IV was eventually released in 1962, first for the IBM 7030 ("Stretch") computer. If you were more familiar with Fortran, you would not have quite as much difficulty as you are. These are the “double precision” types described in the Fortran 90 standard, though that standard does not assign any particular ` KIND= ' value to these types.
Within the PROGRAM statements, your Fortran program can define functions, declare variables to be used in these functions, just like in other programming languages such as R or Python.Within these statements, this is where the calculations on data are performed in the program. We see that Fortran 77 follows the rounding rule that digits 0-4 are rounded downwards while 5-9 are rounded upwards. The type of any constant, variable or array used in a FORTRAN 77 program must be specified either implicitly or explicitly.
The interface block is a powerful structure that was introduced in FORTRAN 90. Leading zeros are not significant in distinguishing statement labels. Any legal Fortran identifier.
This is an arithmetic if statement from FORTRAN 77. 1 A Fortran program starts with the keyword PROGRAM followed by program name, 2 This is followed by the IMPLICITNONE statement (avoid use of implicit type declaration in Fortran 90), 3 Followed by specification statements for various type declarations, 4 Followed by the actual execution statements for the program, 5 Any optional subprogram. Adapted from the FORTRAN 77 specification (emphasis mine):.
They must be given the TARGET attribute in a type statement. IF (e) s1 , s2 , s2. Is placed in column 6.
Obj allocate(obj, source=higher_type(1,2)) Type compatability descends through a chain of children, but a type may extend only one other type. Symbolic names, including those declared in type statements, have the scope of the program unit in which they are included. 1991, Fortran Standard, 6.3.1, 6.3.3 Fortran 90 Handbook, 6.5.1, 6.5.3 Programmer's Guide to Fortran 90, 4.1.5, 8.1.3.
You want to keep track of your books in a library, you might want to track the following attributes about each book − Title;. Type FUNCTION function-name (arg1, arg2, , argn) IMPLICIT NONE specification part execution part subprogram part END FUNCTION function-name ztypeis a Fortran 90 type (is a Fortran 90 type (ege.g., INTEGERINTEGER, REAL, LOGICAL, etc) with or without KIND. A type statement can be used to:.
A(3) end type mytype To create a variable of type mytype, use type (mytype) var An array of mytype can also be created. I, j(100), k(,) Why can't you associate Fortran pointers with any variable having the same type. INTEGER, REAL, COMPLEX, LOGICAL and CHARACTER.
The USE statement removes the need for the INCLUDE statement to make the globals available consistently throughout the program. Using GNU Fortran For gcc version 10.1.0 (GCC) The gfortran team. When used, it gives a calling procedure the full knowledge of the types and characteristics of the dummy arguments that are used inside of the procedure that it references.
This form of input-output is free format I/O, and it is called list-directed input-output. Vi Intel Fortran Language Reference FORALL Statement and Construct. If a TYPE IS type guard statement matches the selector, the block following that statement is executed.
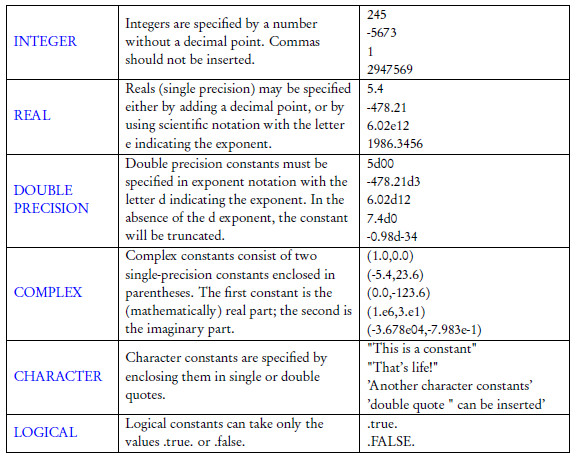
Each of those types can be additionally characterized by a kind which defines internal representation of the type. But it is perfectly fine to use the same format statement for many different write statements. Integers are usually stored as 32 bits (4 bytes) variables.
Fortran 90 compilers are able to recognize keywords from their “positions” in a statement. Fortran 77 has two different types for floating point variables, called real and double precision. Therefore, all integer variables should take on values in the range -m,m where m is approximately 2*10^9.
Each of those types can be additionally characterized by a kind. ALLOCATED ASSOCIATED To Read More About It:. FUNCTION statement • FUNCTION function-name (formal-argument list) OR • type-identifier FUNCTION function-name (formal-argument list) • Function-name:.
The DOUBLE COMPLEX statement is sometimes encountered:. Recall in section 2, "Objects in Fortran 90/95/03", that each type extension contains an implicit parent object of the same name and type as the parent. A label number cannot extend into or beyond column 6.
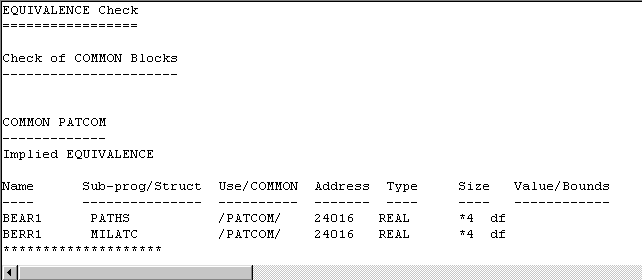
The EQUIVALENCE statement causes two or more items (arrays or variables) to occupy the same memory space. Numeric labels (used for DO loops, FORMAT statements) can be placed anywhere in col's 1-5. For the three numeric types, it defines the precision and range, and for the other two, the specifics of.
Otherwise, if exactly one CLASS IS type guard statement matches the. The SAVE attribute may be declared in the specification part of a module. In the early forms of Fortran the only mechanism for creating global variable store visible from subroutines and functions is to use the COMMON block mechanism.
Example is the namespace name type type1 !. This permitted sequences of variables to be names and shared in common. The syntax of a type declaration within a record structure is identical to that of a normal Fortran type statement.
A program unit can contain type statements that begin with identical keywords. Specify dimension information for an array, or confirm the type of an intrinsic function. Variables represent data or values used in your program.
Although a type may override a type-bound procedure, it is still possible to invoke the version defined by a parent type. A, b(1000), c(10,10) integer, target ::. Types of loop statements Running index (For-loops) Condition-based (While-loops) FOR-loops (Fortran:.
ZHowever, avoid the use of Fortran 90 keywords as identifiers to minimize confusion. ALLOCATABLE Attribute and Statement Dynamic Objects NULLIFY Statement POINTER Attribute and Statement Pointers Related Intrinsics:. The Type statement can be used only at the module level.
E is an integer, real, or double precision expression s1, s2, and s3 are each the statement label of an executable statement that appears in the same program unit as the arithmetic IF statement. Derived data types are used to represent a record. N of 4 thus corresponds to types that occupy four times as much storage as the default types, n of 8 to types that occupy eight times as much storage, and so on.
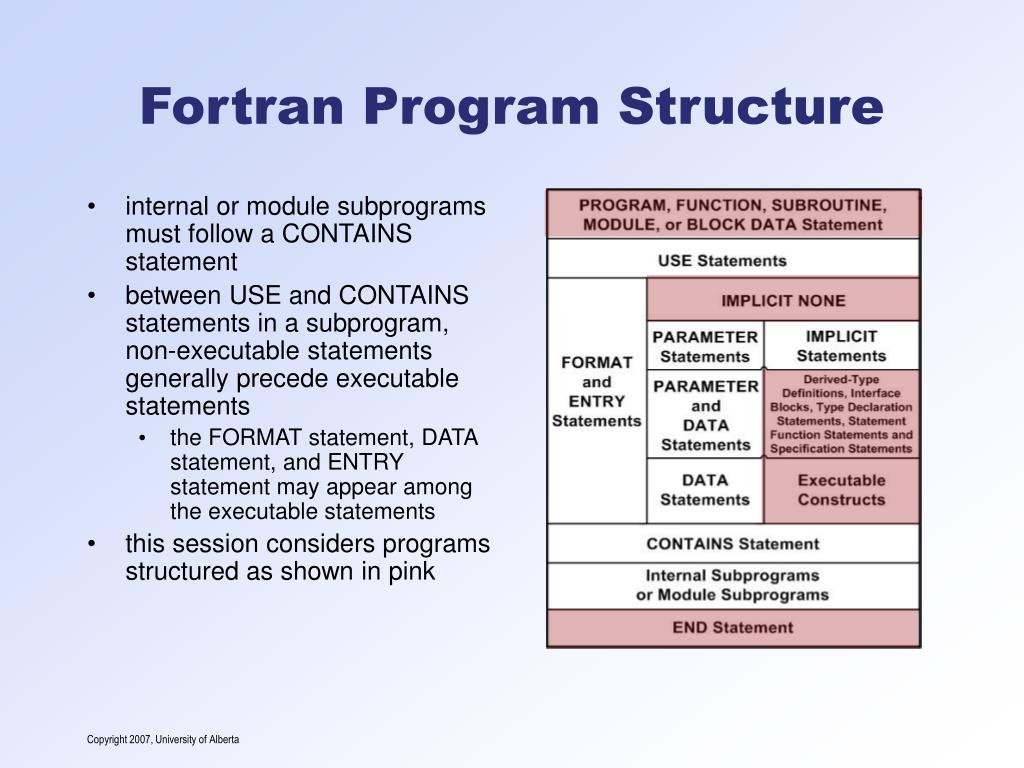
If you do not explicitly list a name in a type statement, then the first letter of the name determines the data type implicitly. PROGRAM statement variable declarations (optional) executable statements END statement SUBROUTINE or FUNCTION modules (optional) The original FORTRAN programs were prepared on a keypunch machine which punched holes into paper cards which had 80 characters maximum. The block to be executed is selected as follows:.
LF Fortran for .NET:. In addition to named common blocks there may also be a blank (unnamed) common block. The syntax for declaring a derived type, is type mytype integer::.
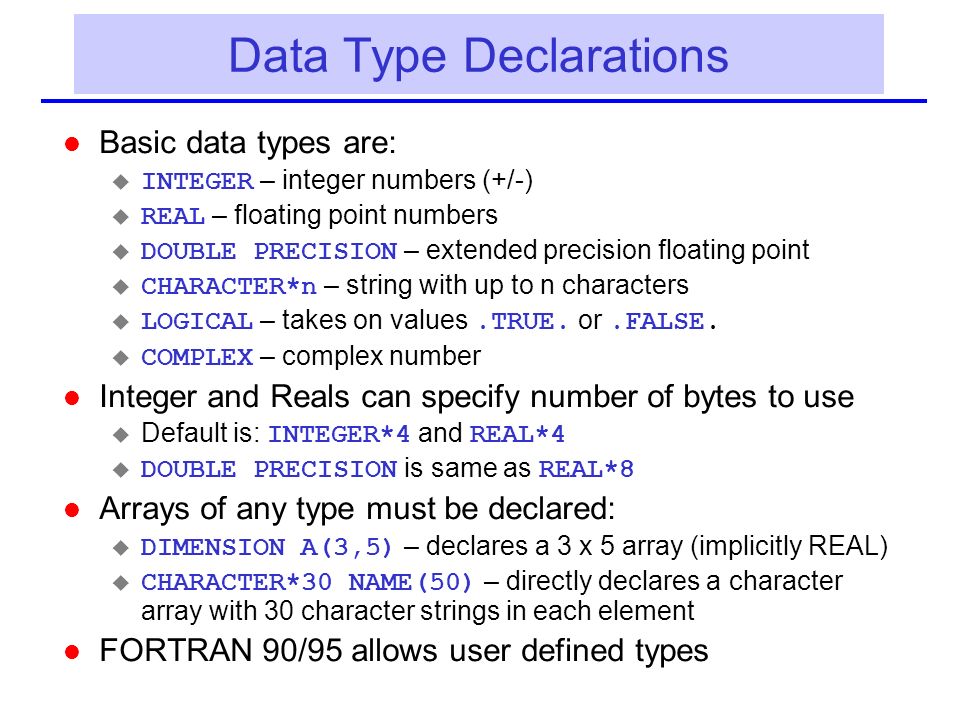
Fortran has five intrinsic data types:. In implicit typing, all constants, variables and arrays beginning with the letters I, J, K, L, M, or N are automatically taken to be. Next Page We have so far seen that we can read data from keyboard using the read * statement, and display output to the screen using the print* statement, respectively.
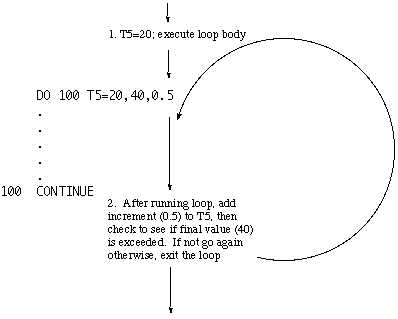
Identifier or a list of identifiers separated by commas – Formal or dummy arguments – Receive information from the main program. The older syntax forms using line number will NOT be discussed !!!) DO variable = startValue, StopValue , StepValue one or more statments END DO:. Fortran Reference Guide Version | iii Chapter 2.
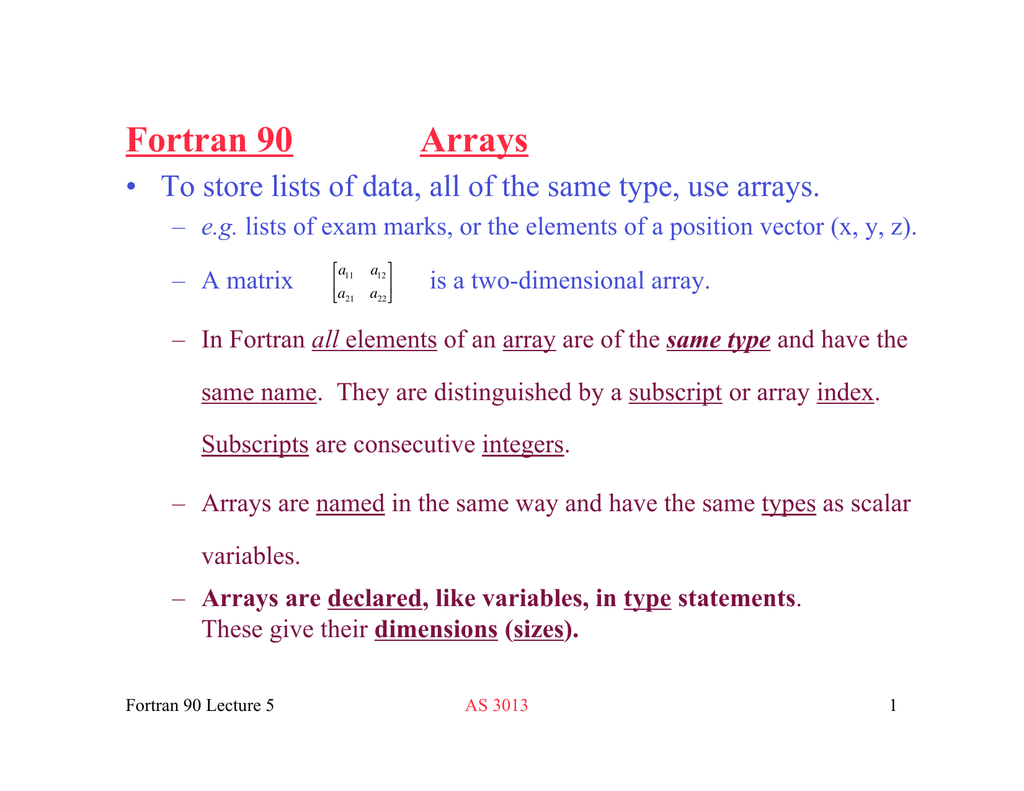
Arrays can have up to 7 dimensions, specified within ( ) parenthesis. The first step in using Fortran pointers is to determine the variables to which you will need to associate pointers. Fortran has five intrinsic data types:.
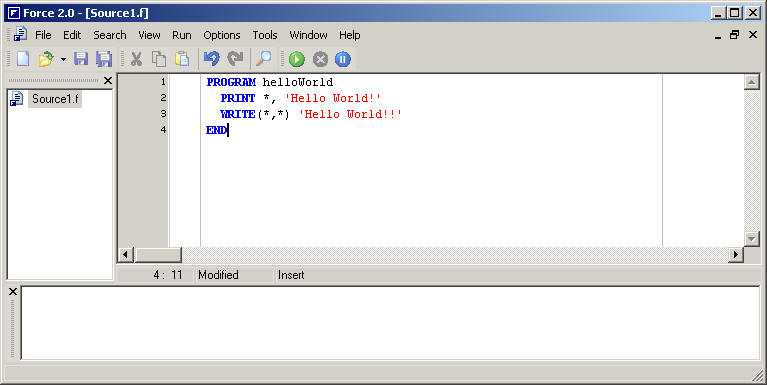
Type can be preceded by either AUTOMATIC or STATIC. This program prints "HELLO, WORLD" to Fortran unit number 6, which on most machines was the line printer or terminal.

Modernizing Old Fortran In Fortran Wiki

Lahey Lf Pro 7 5

Allocate Multiple Arrays With Single Shape Stack Overflow

Fortran 90 Tutorial Grdelin

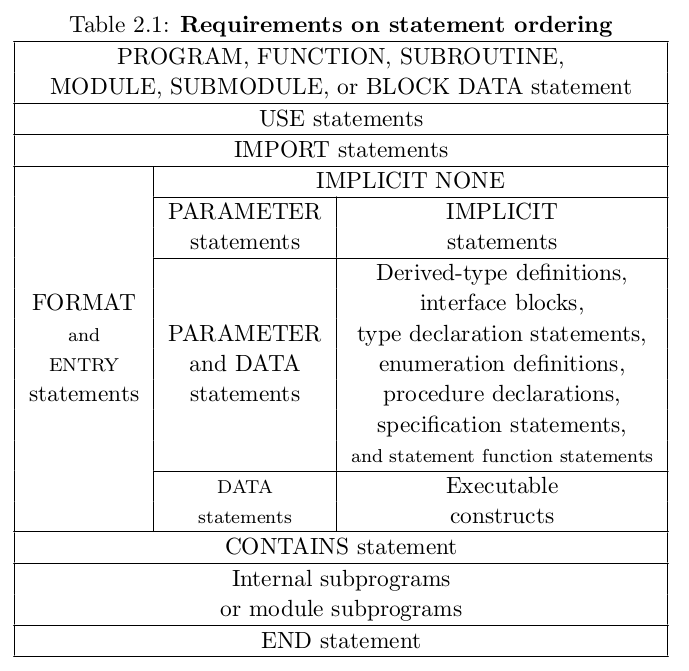
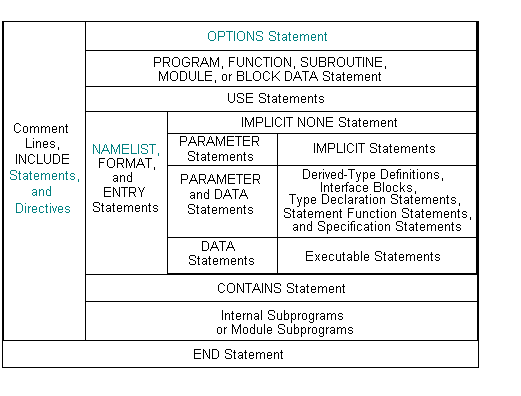
Statement Ordering
C Fortran Binding

Intr Fortran90
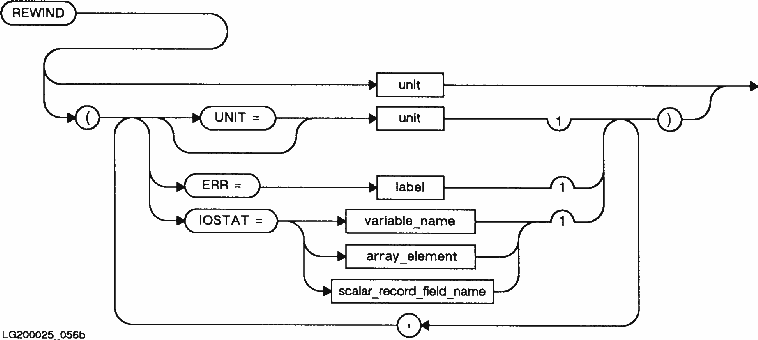
Rewind Statement Executable Hp Fortran 77 Ix Reference

Fortran Theory And Basic Linux Fundamentals
Fortran Iv Reference Page
Winfpt A First Tutorial Fortran Q A Analysis

User Defined Functions Fortran Programming Lecture Notes Docsity
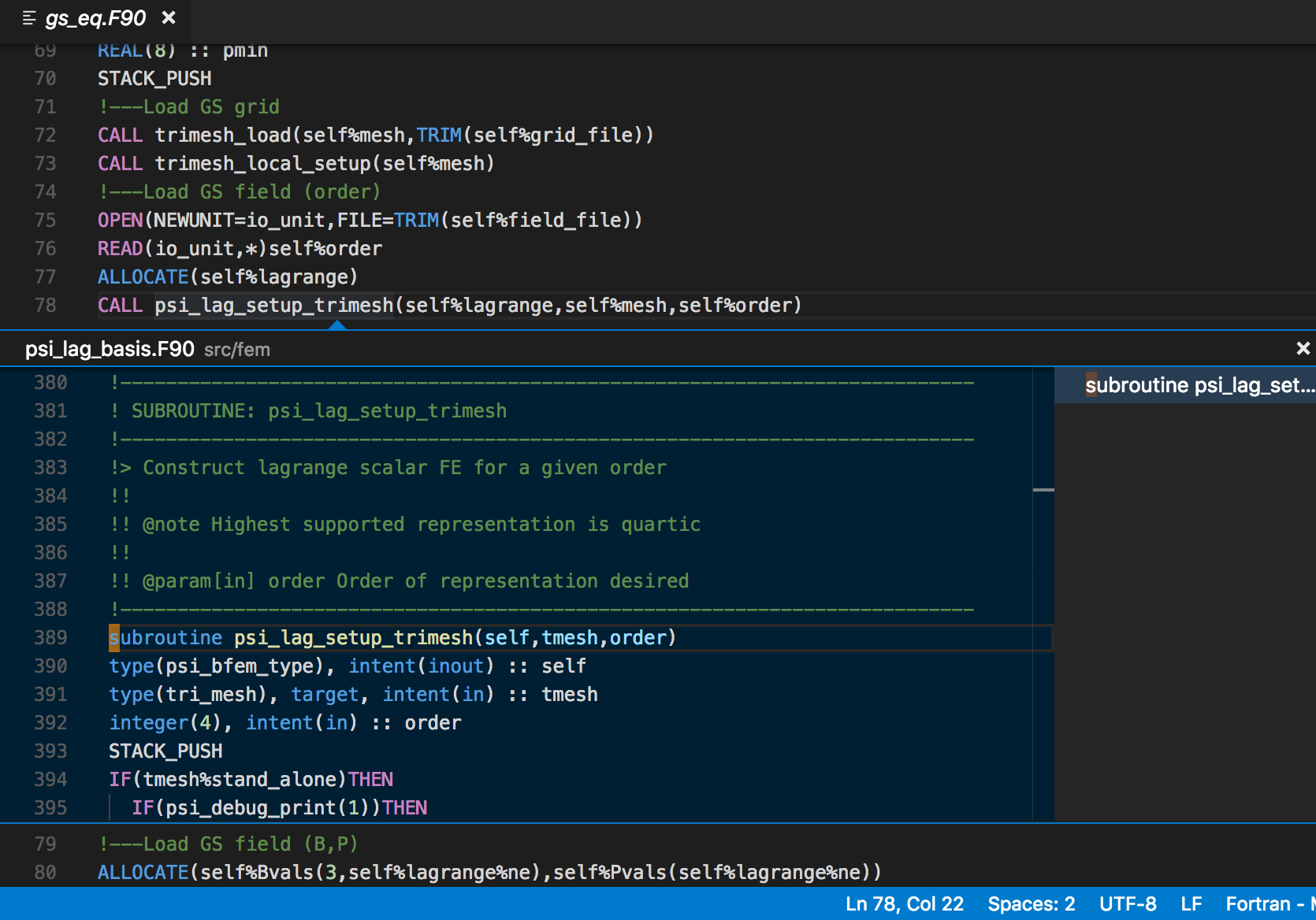
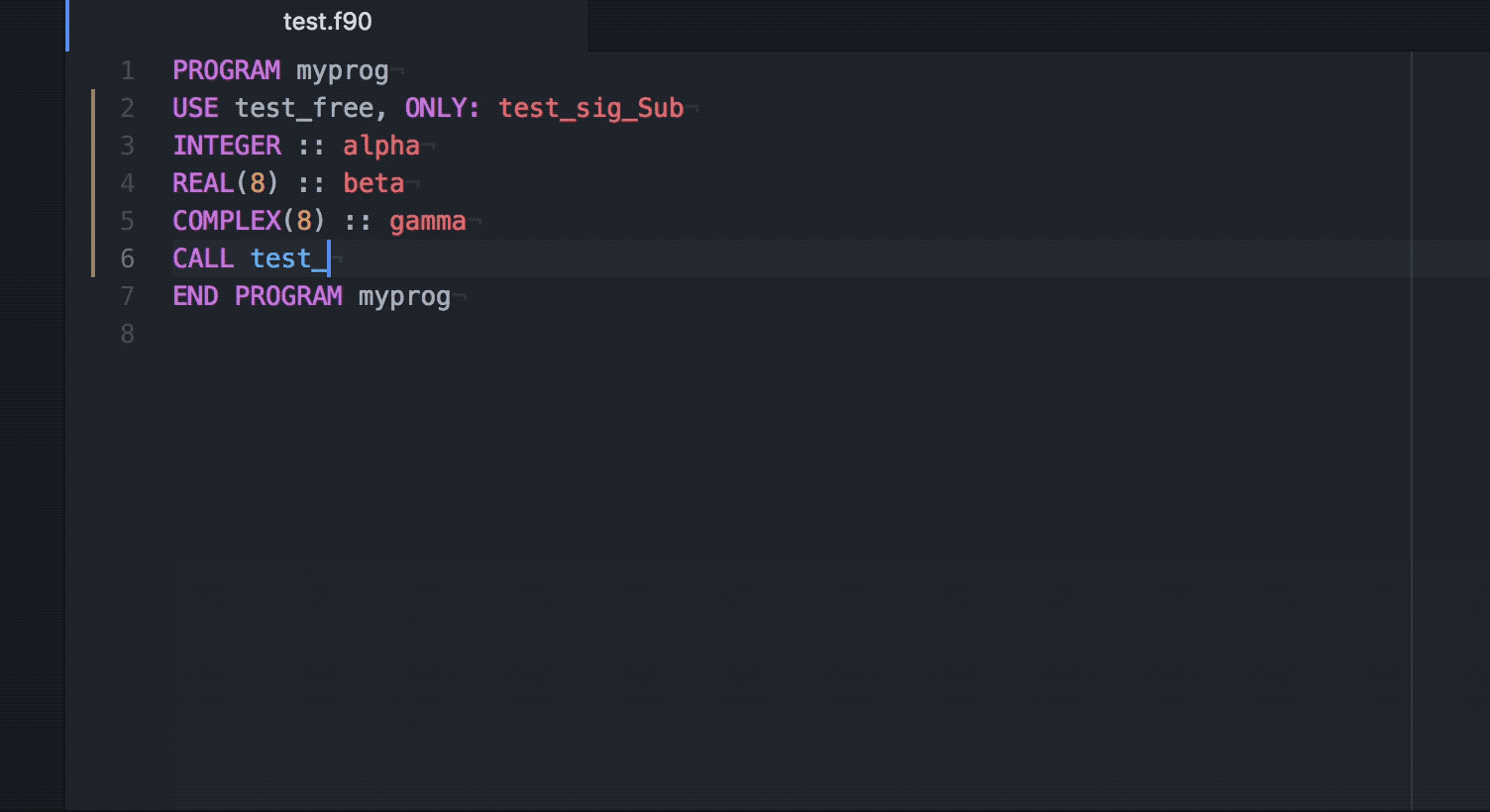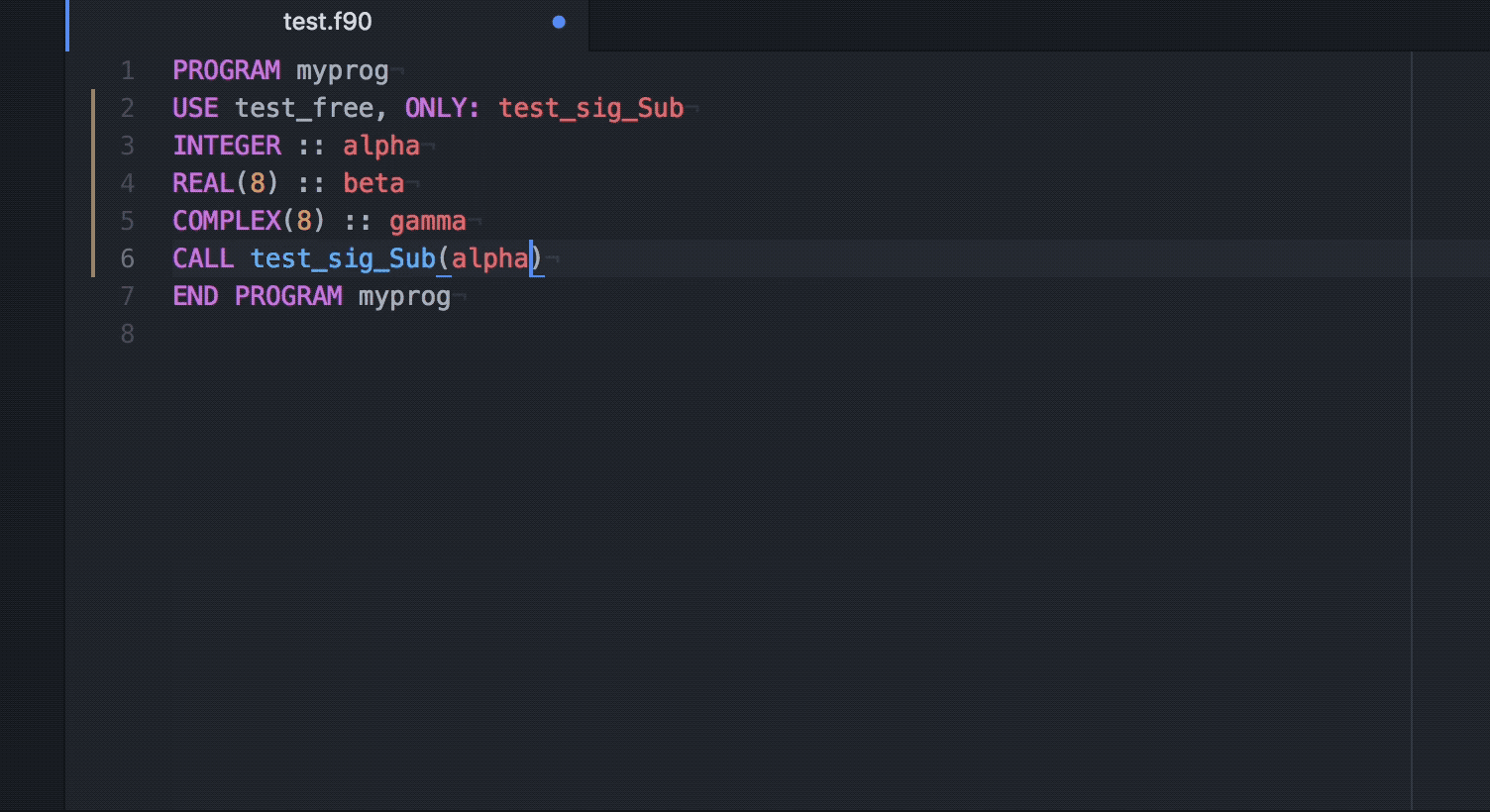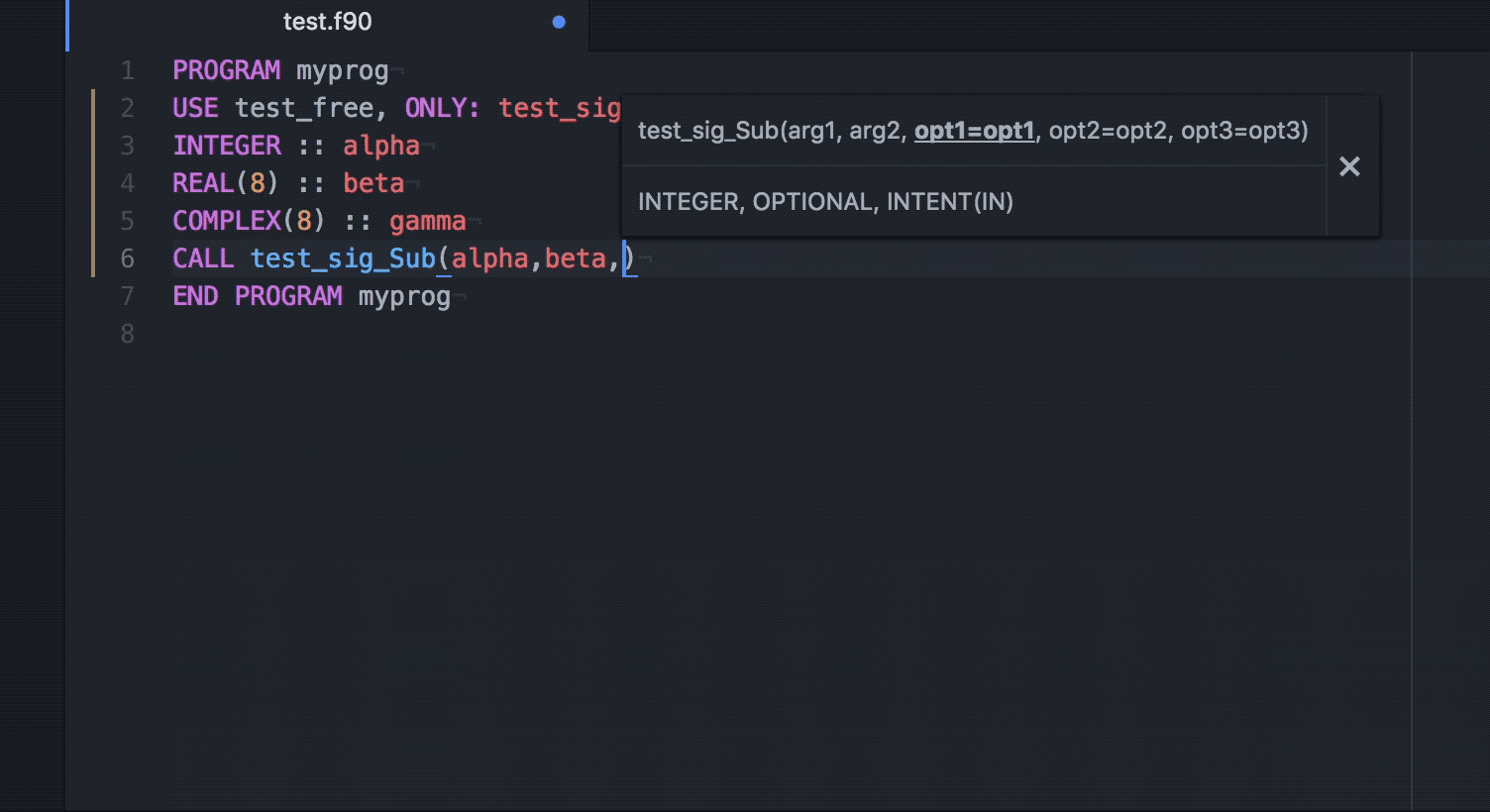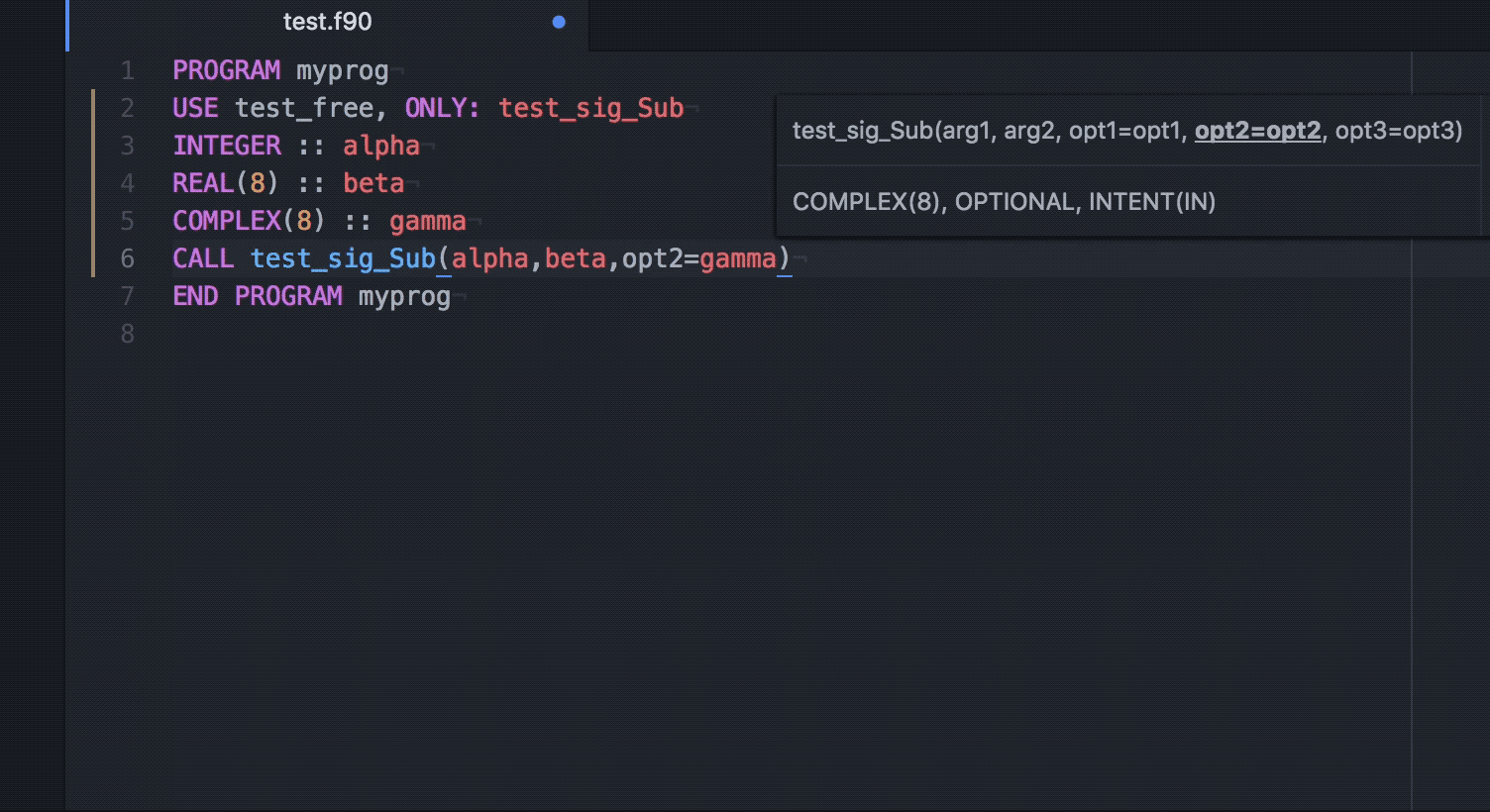
Fortran Intellisense Visual Studio Marketplace

Example Illustrating The Design Of The Fem I O Emulation A Fortran Download Scientific Diagram

Lahey Lg Fortran

Introduction To Fortran 90 Variables And Statements Qub
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrgwp M9wyjd54rii0 S3nn3wftqlo Rstqtuxscc5g2rkkvkwh Usqp Cau
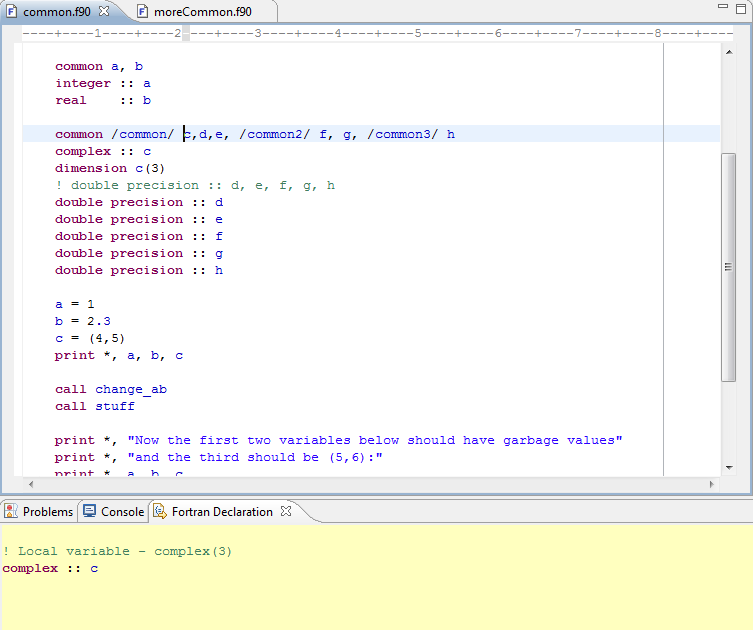
Ptp Photran Documentation Photran6advanced Eclipsepedia

Unclassifiable Statement In Fortran Using Matrix Stack Overflow

What S The Difference Between Fortran Now And Then Electronic Design
Introduction To Fortran Ppt Video Online Download

An Introduction To Pointers Springerlink

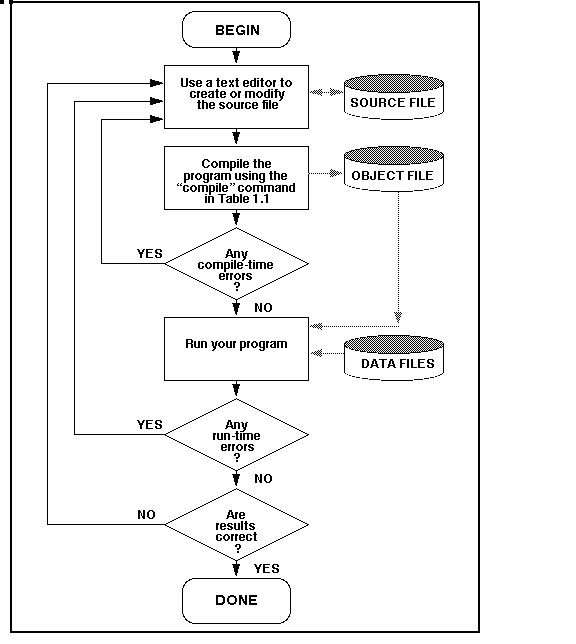
Statements
Introduction To Fortran Ppt Video Online Download

Atlas The T3 Fortran Reference Manual July 1967
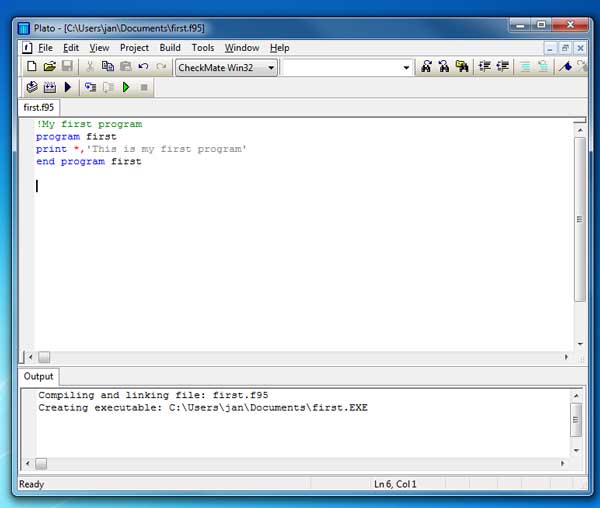
Fortran Tutorial Free Guide To Programming Fortran 90 95 Introduction

Fortran 90 Basics
2
Ide Fortran
Www Livephysics Com Computational Physics Fortran Fortran Statement
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq4h Yoflk8o1if Josdjankl0bezbx26qpkw Usqp Cau
2
Exercice Fortran90 A Resoudre Fortran
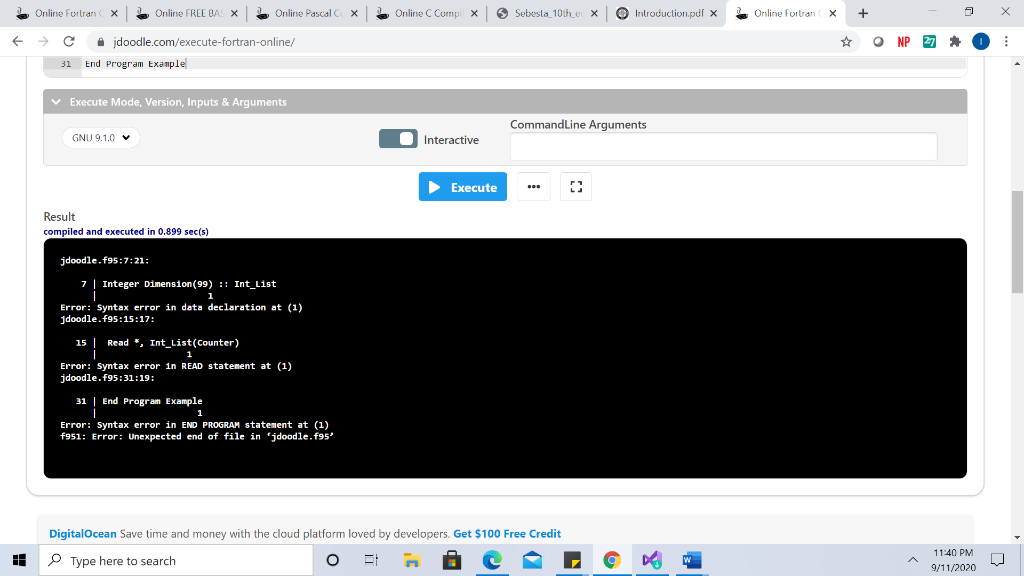
Solved I Ran This Program With The Online Fortran Compile Chegg Com

How To Program In Fortran With Pictures Wikihow

The Fortran 90 Programming Language Book Chapter Iopscience

L10 Fortran Programming Part 2 1 Control Structures Pages 1 10 Text Version Anyflip

Fortran Wikipedia
Fortran s Org 19 Fortranbenefitssurvey Final Pdf
Introduction To Fortran Ppt Download
Ppt Introduction To Fortran Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Introduction To Fortran Ppt Download

Img004 Gif
Byte Statement Nonexecutable Hp Fortran 77 Ix Reference
Apps Dtic Mil Dtic Tr Fulltext U2 A Pdf
2

The Fortran 90 Programming Language Book Chapter Iopscience
Programming Languages

Fortran 90

Fortran Select Case Construct Tutorialspoint
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsbhb4gmauz61iqpgfsktmbrntimipma Fngmyqzunyx3ebvr 1 Usqp Cau
Fortran 77

Statements

Phys345 Introduction To Computations In Physics Section 4 Compiled Languages Programming Fortran Lecture 2 Introduction
Ppt Introduction To Fortran Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Fortran 90 Basics

Img002 Gif
2
Fortran Wikiwand
2
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqlcdr4gopo7x9pxdnfhextplacsb59vbdwtvw4bw3nvp6cycum Usqp Cau
Fortran 90 Arrays

Fortran Re Engineering Example 4 The Craft Of Coding
Installing And Getting Started In Fortran Using G95 Compiler Steemit

Intel Visual Fortran Compiler 19 0 For Windows Release Notes For

Pdf Fortran 77 Tutorial Akmal Saad Academia Edu

Fortran Wikipedia
Fortran Formula Tranlastion

What S The Difference Between Fortran Now And Then Electronic Design

Lahey Elf90 Details

Introduction To Fortran

Pdf The Nestor Library A Tool For Implementing Fortran Source To Source Transfromations
Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 003 Implicit None Simple Data Types Youtube
2
Fortran Programming Tutorials Revised 003 Implicit None Simple Data Types Youtube

Fortran 90
Getting Started With Fortran

Ppt Fortran 90 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Walk Through Flang Part 3

Fortran Ppt Subroutine Array Data Structure

Fortran Loops Tutorialspoint
Solved 09 Which Of The Follow Ing Is Not Correct Statemen Chegg Com

Fortran 90 95 Programming Manual Pdf Free Download

Github Stanislavradkov Fortran Cheat Sheet Fortran Cheat Sheet
Forty Years Of Computer Languages The Old Fortran
Statements
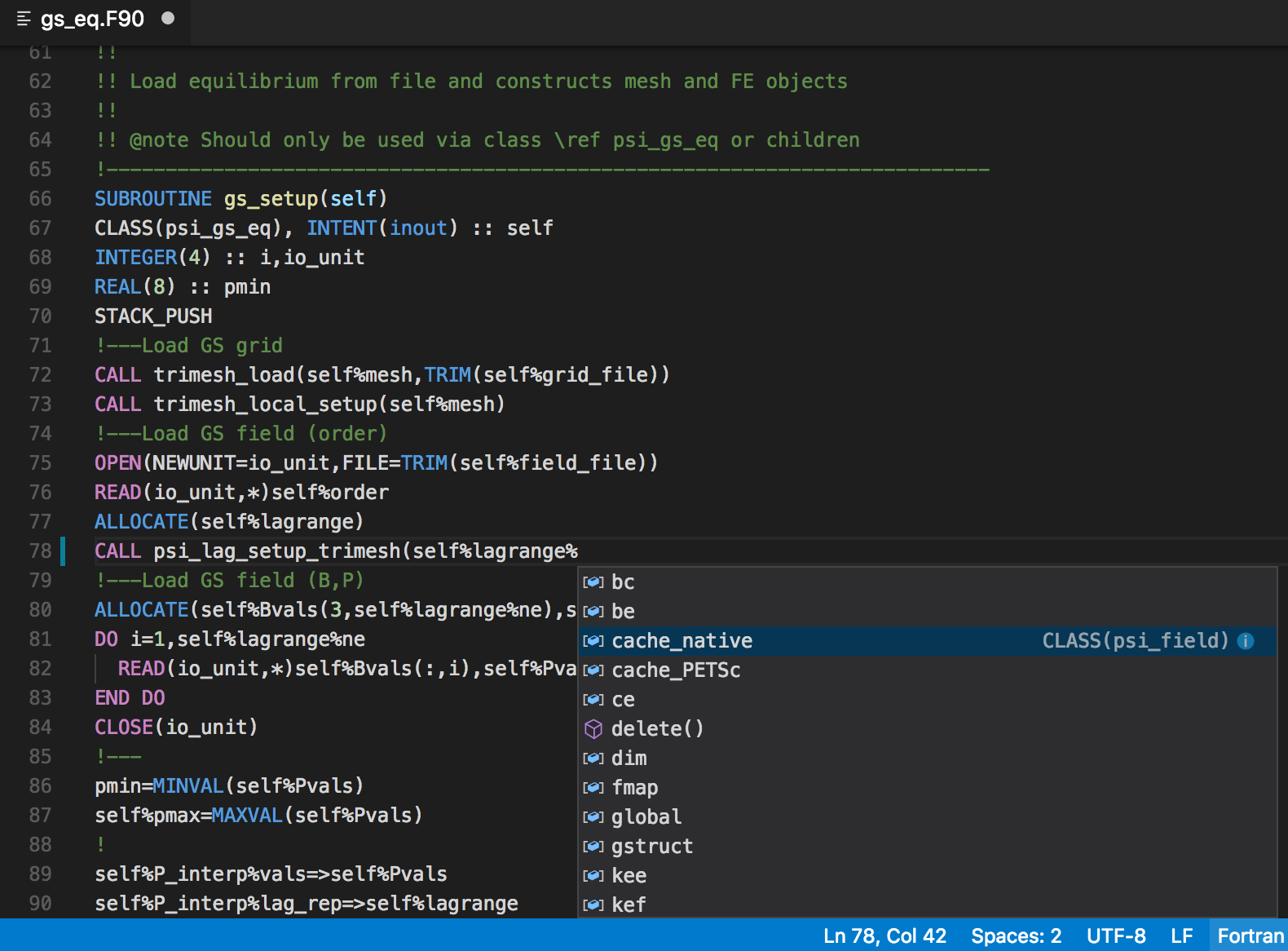
Fortran Intellisense Visual Studio Marketplace
2
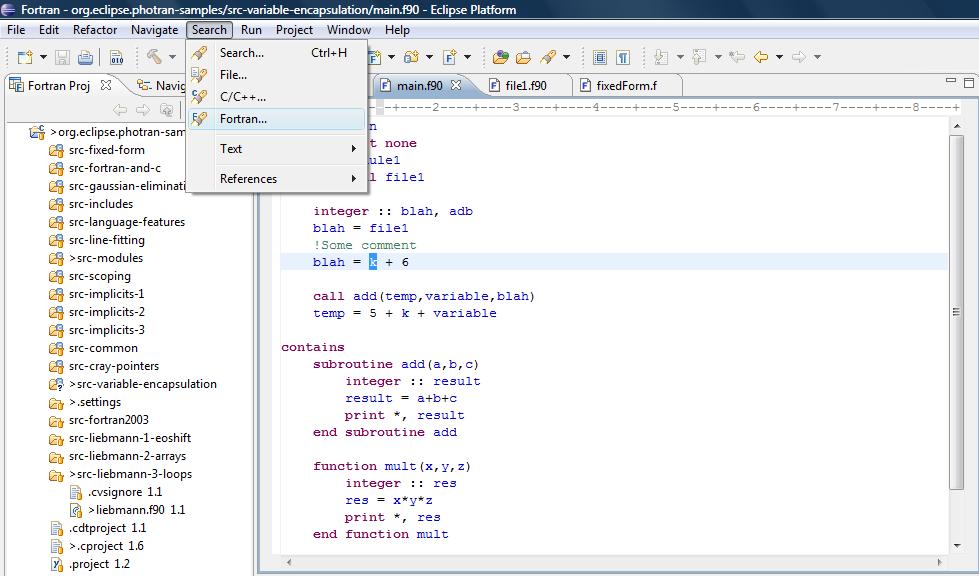
Ptp Photran Documentation Photran6advanced Eclipsepedia

Fortran Iv Reference Page
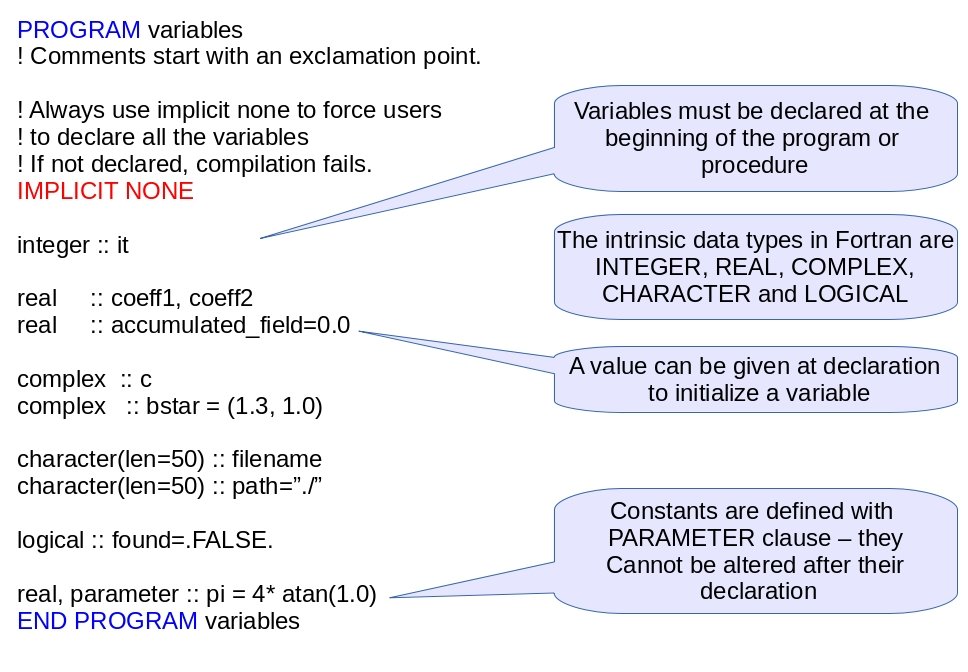
Getting Started With Fortran

Fortran 90 For Scientists And Engineers Fortran 90 For Scientists And Engineers Docsity

How To Program In Fortran With Pictures Wikihow
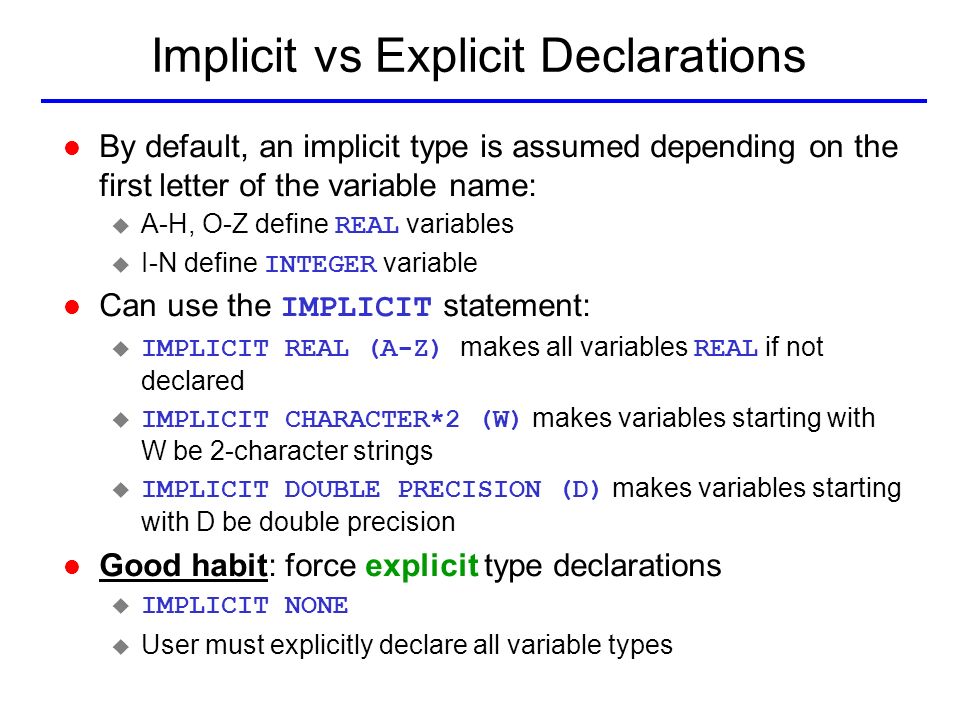
Introduction To Fortran Ppt Video Online Download

Fortran Data Base Facility Ver 1 Ref Man 6040d Oct80 Pdf
Resolve A Doi
Http Homepage Ntu Edu Tw Wttsai Fortran Ppt 2 Basic Elements Of Fortran Pdf

Table I From K Scope A Java Based Fortran Source Code Analyzer With Graphical User Interface For Performance Improvement Semantic Scholar



